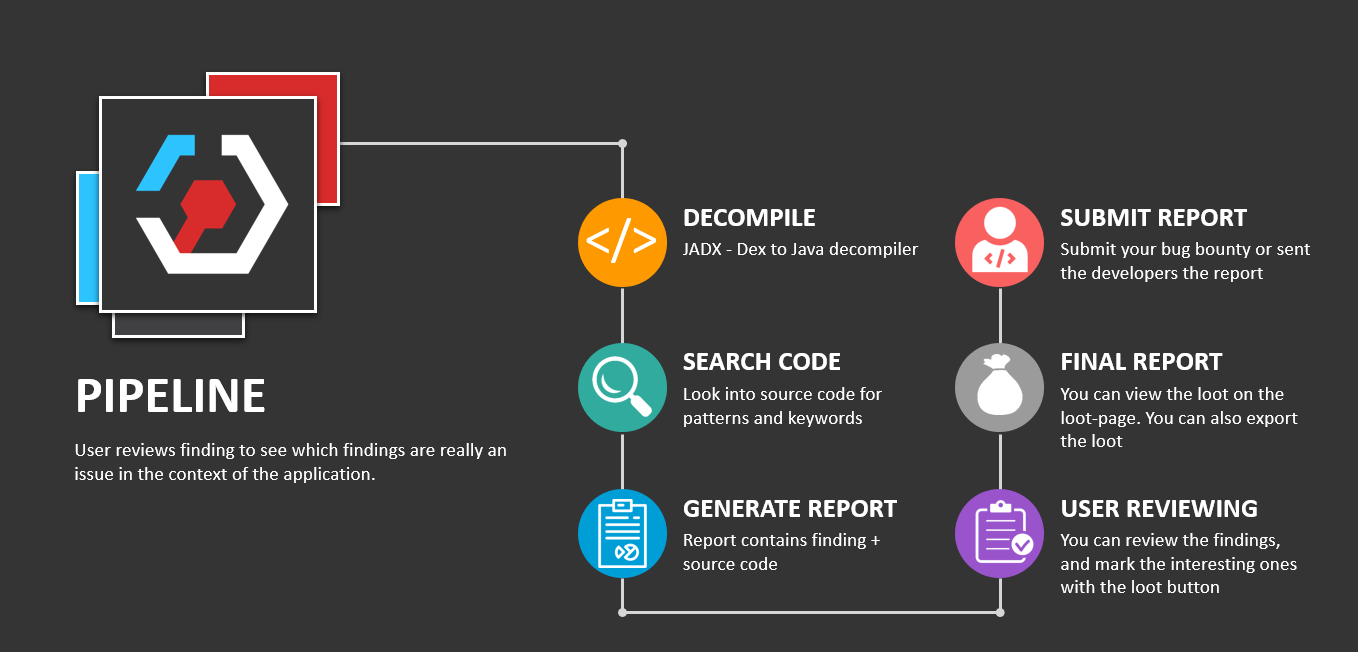
Android アプリケーションのPentesting
{{#include ../../banners/hacktricks-training.md}}
Android アプリケーションの基本
このページは、Android セキュリティに関連する最も重要な部分と、Android アプリケーション内で最も危険なコンポーネントについて知るために、まず読むことを強くおすすめします:
{{#ref}} android-applications-basics.md {{#endref}}
ADB (Android Debug Bridge)
これは、エミュレートされたものでも実機でも、Android デバイスに接続するために必要な主要なツールです。
ADB を使用すると、コンピュータから USB または Network 経由でデバイスを制御できます。このユーティリティは、ファイルの双方向の コピー、アプリの インストール と アンインストール、シェルコマンドの 実行、データの バックアップ、ログの 読み取り などの機能を提供します。
adb の使い方を学ぶには、以下の ADB Commands のリストを参照してください。
Smali
時には、アプリケーションのコードを修正して 隠された情報(難読化されたパスワードやフラグなど)にアクセスすることが有益です。その場合、apk をデコンパイルしてコードを修正し、再コンパイルすることが考えられます。
In this tutorial you can learn how to decompile and APK, modify Smali code and recompile the APK with the new functionality。これは、これから紹介する動的解析におけるいくつかのテストに対する代替手段として非常に役立つ可能性があります。したがって、この可能性を常に念頭に置いてください。
その他の興味深いトリック
- Spoofing your location in Play Store
- Shizuku Privileged API (ADB-based non-root privileged access)
- Exploiting Insecure In-App Update Mechanisms
- Abusing Accessibility Services (Android RAT)
- Download APKs: https://apps.evozi.com/apk-downloader/, https://apkpure.com/es/, https://www.apkmirror.com/, https://apkcombo.com/es-es/apk-downloader/, https://github.com/kiber-io/apkd
- デバイスからAPKを抽出する:
adb shell pm list packages
com.android.insecurebankv2
adb shell pm path com.android.insecurebankv2
package:/data/app/com.android.insecurebankv2-Jnf8pNgwy3QA_U5f-n_4jQ==/base.apk
adb pull /data/app/com.android.insecurebankv2-Jnf8pNgwy3QA_U5f-n_4jQ==/base.apk
- すべての splits と base apks を APKEditor でマージする:
mkdir splits
adb shell pm path com.android.insecurebankv2 | cut -d ':' -f 2 | xargs -n1 -i adb pull {} splits
java -jar ../APKEditor.jar m -i splits/ -o merged.apk
# after merging, you will need to align and sign the apk, personally, I like to use the uberapksigner
java -jar uber-apk-signer.jar -a merged.apk --allowResign -o merged_signed
ケーススタディと脆弱性
{{#ref}} ../ios-pentesting/air-keyboard-remote-input-injection.md {{#endref}}
{{#ref}} ../../linux-hardening/privilege-escalation/android-rooting-frameworks-manager-auth-bypass-syscall-hook.md {{#endref}}
静的解析
まず、APKを解析するには、decompiler を使ってJava コードを確認するべきです。
Please, read here to find information about different available decompilers.
興味深い情報の探索
APKのstringsを確認するだけで、passwords、URLs (https://github.com/ndelphit/apkurlgrep)、api keys、encryption、bluetooth uuids、tokens などを検索できます。コード実行のbackdoorsや認証用のbackdoors(hardcoded admin credentials to the app)さえ探してください。
Firebase
firebase URLsに特に注意し、設定が不適切でないか確認してください。More information about whats is FIrebase and how to exploit it here.
アプリケーションの基本的理解 - Manifest.xml, strings.xml
アプリケーションの Manifest.xml および strings.xml ファイルの調査は潜在的なセキュリティ脆弱性を明らかにすることがあります。これらのファイルは decompiler を使うか、APK の拡張子を .zip に変更して解凍することでアクセスできます。
Manifest.xml から特定できる 脆弱性 には次のものがあります:
- Debuggable Applications: Manifest.xml で
debuggable="true"に設定されたアプリケーションは、接続を許可してしまい、悪用に繋がるリスクがあります。デバッガブルなアプリをデバイス上で見つけて悪用する方法についてはチュートリアルを参照してください。 - Backup Settings:
android:allowBackup="false"属性は、usb debugging が有効な場合などに adb 経由でのデータバックアップによる不正アクセスを防ぐため、機密情報を扱うアプリでは明示的に false に設定する必要があります。 - Network Security:
android:networkSecurityConfig="@xml/network_security_config"のようなカスタムネットワークセキュリティ設定(res/xml/ 内)は、証明書ピンや HTTP トラフィックの許可設定などのセキュリティ詳細を指定できます。例えば特定ドメインへの HTTP トラフィックを許可する設定などがあります。 - Exported Activities and Services: マニフェスト内でエクスポートされた activities や services を特定することで、悪用される可能性のあるコンポーネントが明らかになります。動的テスト中にこれらをさらに解析すると、どのように悪用できるかが分かります。
- Content Providers and FileProviders: 公開された content providers はデータへの不正アクセスや変更を許す可能性があります。FileProviders の設定も詳しく調べるべきです。
- Broadcast Receivers and URL Schemes: これらのコンポーネントは悪用の足がかりになり得ます。特に URL スキームの扱い方が入力に対する脆弱性を生まないか注意してください。
- SDK Versions:
minSdkVersion、targetSDKVersion、maxSdkVersion属性はサポートする Android バージョンを示します。古く脆弱な Android バージョンをサポートし続けることの危険性が分かります。
strings.xml からは、API keys、カスタムスキーマ、その他の開発者メモなどの機密情報が見つかることがあり、これらのリソースは慎重に確認する必要があります。
Tapjacking
Tapjacking は、malicious application を起動して 被害アプリの上に自身を配置する攻撃です。被害アプリを視覚的に覆った後、マルウェアの UI はユーザーを騙して操作させるように設計されており、その操作を被害アプリに転送します。結果として、ユーザーは実際には被害アプリ上で操作を行っていることに気付かなくなります。
Find more information in:
{{#ref}} tapjacking.md {{#endref}}
Task Hijacking
launchMode が singleTask に設定され、かつ taskAffinity が定義されていない activity は Task Hijacking の脆弱性があります。つまり、別のapplicationをインストールしてそれを本物のアプリより先に起動すると、本物のアプリの task を乗っ取ってしまう可能性があり(ユーザーは本物のアプリを使っているつもりで実は悪意あるアプリを操作している)、その結果ユーザーを騙すことができます。
More info in:
{{#ref}} android-task-hijacking.md {{#endref}}
不適切なデータ保存
内部ストレージ
Android では、internal ストレージに保存されたファイルはそれを作成したアプリだけがアクセスできるよう設計されています。このセキュリティ対策は Android OS によって強制され、ほとんどのアプリのセキュリティ要件には十分です。ただし、開発者が MODE_WORLD_READABLE や MODE_WORLD_WRITABLE のようなモードを利用してファイルを異なるアプリ間で共有できるようにする場合があります。しかし、これらのモードは他のアプリ(潜在的に malicious なものを含む)によるファイルへのアクセスを制限しません。
- Static Analysis:
MODE_WORLD_READABLEとMODE_WORLD_WRITABLEの使用は慎重に精査してください。これらのモードはファイルを意図しない、または不正なアクセスに晒す可能性があります。
- Dynamic Analysis:
- アプリが作成するファイルのパーミッションを確認してください。特に、ファイルが world-readable や world-writable に設定されていないかをチェックします。これが有効だと、デバイスにインストールされた任意のアプリがこれらのファイルを読み書きできてしまうため重大なセキュリティリスクを生じます。
外部ストレージ
SD カードのような external storage 上のファイルを扱う際には、以下の点に注意してください:
- Accessibility:
- 外部ストレージ上のファイルはグローバルに読み書き可能です。つまり、任意のアプリやユーザーがアクセスできます。
- Security Concerns:
- このような容易なアクセス性のため、機密情報を外部ストレージに保存しないことが推奨されます。
- 外部ストレージは取り外し可能であり、任意のアプリからアクセスされ得るため、セキュリティ的に不利です。
- Handling Data from External Storage:
- 外部ストレージから取得したデータは常に入力検証を行ってください。外部ストレージのデータは信頼できないソースと見なすべきです。
- 外部ストレージに実行可能ファイルや class ファイルを置いて動的にロードすることは強く非推奨です。
- どうしても外部ストレージから実行可能ファイルを取得する必要がある場合、それらのファイルが署名され、暗号的に検証済みであることを確認してから動的にロードしてください。これはアプリケーションのセキュリティ整合性を維持する上で重要です。
外部ストレージには /storage/emulated/0 , /sdcard , /mnt/sdcard からアクセスできます。
Tip
Android 4.4(API 17)以降、SD カードはディレクトリ構造を持ち、アプリからはそのアプリ専用のディレクトリへのアクセスのみが制限されるようになりました。これにより、悪意あるアプリが別のアプリのファイルに対して読み書きアクセスを得ることを防ぎます。
平文で保存された機密データ
- Shared preferences: Android は各アプリが
/data/data/<packagename>/shared_prefs/に簡単に xml ファイルを保存できるようにしており、そのフォルダ内に平文で機密情報が見つかることがあります。 - Databases: Android は各アプリが
/data/data/<packagename>/databases/に sqlite データベースを保存できるようにしており、そのフォルダ内に平文で機密情報が見つかることがあります。
Broken TLS
Accept All Certificates
なぜか開発者が全ての証明書を受け入れてしまうことがあります。例えばホスト名が一致しない場合でも、次のようなコード行で全てを受け入れてしまうことがあります:
SSLSocketFactory sf = new cc(trustStore);
sf.setHostnameVerifier(SSLSocketFactory.ALLOW_ALL_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER);
A good way to test this is to try to capture the traffic using some proxy like Burp without authorising Burp CA inside the device. Also, you can generate with Burp a certificate for a different hostname and use it.
Broken Cryptography
Poor Key Management Processes
一部の開発者はセンシティブなデータをローカルストレージに保存し、コード内にハードコーディング/予測可能なキーで暗号化しています。reversing によって攻撃者が機密情報を抽出できる可能性があるため、これは避けるべきです。
Use of Insecure and/or Deprecated Algorithms
開発者は認証チェック、データの保存や送信に deprecated algorithms を使うべきではありません。例としては RC4、MD4、MD5、SHA1 などがあります。例えばパスワード保存に hashes を使う場合は、salt を用いた brute-force 抵抗性のあるハッシュを使うべきです。
Other checks
- It's recommended to obfuscate the APK to difficult the reverse engineer labour to attackers.
- If the app is sensitive (like bank apps), it should perform it's own checks to see if the mobile is rooted and act in consequence.
- If the app is sensitive (like bank apps), it should check if an emulator is being used.
- If the app is sensitive (like bank apps), it should check it's own integrity before executing it to check if it was modified.
- Use APKiD to check which compiler/packer/obfuscator was used to build the APK
React Native Application
Read the following page to learn how to easily access javascript code of React applications:
{{#ref}} react-native-application.md {{#endref}}
Xamarin Applications
Read the following page to learn how to easily access C# code of a xamarin applications:
{{#ref}} ../xamarin-apps.md {{#endref}}
Superpacked Applications
According to this blog post superpacked is a Meta algorithm that compress the content of an application into a single file. The blog talks about the possibility of creating an app that decompress these kind of apps... and a faster way which involves to execute the application and gather the decompressed files from the filesystem.
Automated Static Code Analysis
The tool mariana-trench is capable of finding vulnerabilities by scanning the code of the application. This tool contains a series of known sources (that indicates to the tool the places where the input is controlled by the user), sinks (which indicates to the tool dangerous places where malicious user input could cause damages) and rules. These rules indicates the combination of sources-sinks that indicates a vulnerability.
With this knowledge, mariana-trench will review the code and find possible vulnerabilities on it.
Secrets leaked
An application may contain secrets (API keys, passwords, hidden urls, subdomains...) inside of it that you might be able to discover. You could use a tool such as https://github.com/dwisiswant0/apkleaks
Bypass Biometric Authentication
{{#ref}} bypass-biometric-authentication-android.md {{#endref}}
Other interesting functions
- Code execution:
Runtime.exec(), ProcessBuilder(), native code:system() - Send SMSs:
sendTextMessage, sendMultipartTestMessage - Native functions declared as
native:public native, System.loadLibrary, System.load - Read this to learn how to reverse native functions
Other tricks
{{#ref}} content-protocol.md {{#endref}}
Dynamic Analysis
First of all, you need an environment where you can install the application and all the environment (Burp CA cert, Drozer and Frida mainly). Therefore, a rooted device (emulated or not) is extremely recommended.
Online Dynamic analysis
You can create a free account in: https://appetize.io/. This platform allows you to upload and execute APKs, so it is useful to see how an apk is behaving.
You can even see the logs of your application in the web and connect through adb.
Thanks to the ADB connection you can use Drozer and Frida inside the emulators.
Local Dynamic Analysis
Using an emulator
- Android Studio (You can create x86 and arm devices, and according to this latest x86 versions support ARM libraries without needing an slow arm emulator).
- Learn to set it up in this page:
{{#ref}} avd-android-virtual-device.md {{#endref}}
- Genymotion (Free version: Personal Edition, you need to create an account. It's recommend to download the version WITH VirtualBox to avoid potential errors.)
- Nox (Free, but it doesn't support Frida or Drozer).
Tip
When creating a new emulator on any platform remember that the bigger the screen is, the slower the emulator will run. So select small screens if possible.
To install google services (like AppStore) in Genymotion you need to click on the red marked button of the following image:
Also, notice that in the configuration of the Android VM in Genymotion you can select Bridge Network mode (this will be useful if you will be connecting to the Android VM from a different VM with the tools).
Use a physical device
You need to activate the debugging options and it will be cool if you can root it:
- Settings.
- (FromAndroid 8.0) Select System.
- Select About phone.
- Press Build number 7 times.
- Go back and you will find the Developer options.
Once you have installed the application, the first thing you should do is to try it and investigate what does it do, how does it work and get comfortable with it.
I will suggest to perform this initial dynamic analysis using MobSF dynamic analysis + pidcat, so we will be able to learn how the application works while MobSF captures a lot of interesting data you can review later on.
Magisk/Zygisk quick notes (recommended on Pixel devices)
- Patch boot.img with the Magisk app and flash via fastboot to get systemless root
- Enable Zygisk + DenyList for root hiding; consider LSPosed/Shamiko when stronger hiding is required
- Keep original boot.img to recover from OTA updates; re-patch after each OTA
- For screen mirroring, use scrcpy on the host
Unintended Data Leakage
Logging
Developers should be cautious of exposing debugging information publicly, as it can lead to sensitive data leaks. The tools pidcat and adb logcat are recommended for monitoring application logs to identify and protect sensitive information. Pidcat is favored for its ease of use and readability.
Warning
Note that from later newer than Android 4.0, applications are only able to access their own logs. So applications cannot access other apps logs.
Anyway, it's still recommended to not log sensitive information.
Copy/Paste Buffer Caching
Android's clipboard-based framework enables copy-paste functionality in apps, yet poses a risk as other applications can access the clipboard, potentially exposing sensitive data. It's crucial to disable copy/paste functions for sensitive sections of an application, like credit card details, to prevent data leaks.
Crash Logs
If an application crashes and saves logs, these logs can assist attackers, particularly when the application cannot be reverse-engineered. To mitigate this risk, avoid logging on crashes, and if logs must be transmitted over the network, ensure they are sent via an SSL channel for security.
As pentester, try to take a look to these logs.
Analytics Data Sent To 3rd Parties
Applications often integrate services like Google Adsense, which can inadvertently leak sensitive data due to improper implementation by developers. To identify potential data leaks, it's advisable to intercept the application's traffic and check for any sensitive information being sent to third-party services.
SQLite DBs
Most of the applications will use internal SQLite databases to save information. During the pentest take a look to the databases created, the names of tables and columns and all the data saved because you could find sensitive information (which would be a vulnerability).
Databases should be located in /data/data/the.package.name/databases like /data/data/com.mwr.example.sieve/databases
If the database is saving confidential information and is encrypted but you can find the password inside the application it's still a vulnerability.
Enumerate the tables using .tables and enumerate the columns of the tables doing .schema <table_name>
Drozer (Exploit Activities, Content Providers and Services)
From Drozer Docs: Drozer allows you to assume the role of an Android app and interact with other apps. It can do anything that an installed application can do, such as make use of Android’s Inter-Process Communication (IPC) mechanism and interact with the underlying operating system. .
Drozer is a useful tool to exploit exported activities, exported services and Content Providers as you will learn in the following sections.
Exploiting exported Activities
Read this if you want to refresh what is an Android Activity.
Also remember that the code of an activity starts in the onCreate method.
Authorisation bypass
When an Activity is exported you can invoke its screen from an external app. Therefore, if an activity with sensitive information is exported you could bypass the authentication mechanisms to access it.
Learn how to exploit exported activities with Drozer.
You can also start an exported activity from adb:
- PackageName is com.example.demo
- Exported ActivityName is com.example.test.MainActivity
adb shell am start -n com.example.demo/com.example.test.MainActivity
NOTE: MobSF はアクティビティの android:launchMode に singleTask/singleInstance を使用していると悪意のあるものとして検出しますが、this によると、どうやらこれは古いバージョン(API versions < 21)でのみ危険なようです。
Tip
authorisation bypass が必ずしも脆弱性とは限らないことに注意してください。どのように bypass が動作するか、どの情報が露出するかによります。
機密情報の漏洩
アクティビティは結果を返すこともあります。エクスポートされ保護されていないアクティビティが setResult メソッドを呼び出し、機密情報を返しているのを見つけた場合、機密情報の漏洩が発生しています。
Tapjacking
Tapjacking が防止されていない場合、エクスポートされたアクティビティを悪用してユーザーに予期しない操作をさせることができます。For more info about what is Tapjacking follow the link.
Exploiting Content Providers - Accessing and manipulating sensitive information
Read this if you want to refresh what is a Content Provider.
Content providers は基本的に share data に使用されます。アプリに利用可能な content providers がある場合、それらから extract sensitive データを取り出せる可能性があります。また、脆弱である可能性があるため、SQL injections や Path Traversals のテストを行うことも重要です。
Learn how to exploit Content Providers with Drozer.
Exploiting Services
Read this if you want to refresh what is a Service.
Service の処理は onStartCommand メソッドで始まることを忘れないでください。
Service は基本的にデータを受け取り、それを処理し、応答を(返すこともあれば返さないこともある)ものです。したがって、アプリがいくつかのサービスをエクスポートしている場合は、何をしているのかを理解するためにコードを確認し、機密情報の抽出や認証回避などを動的にテストするべきです。
Learn how to exploit Services with Drozer.
Exploiting Broadcast Receivers
Read this if you want to refresh what is a Broadcast Receiver.
Broadcast Receiver の処理は onReceive メソッドで始まることを忘れないでください。
ブロードキャストレシーバは特定のタイプのメッセージを待ち受けます。受信したメッセージの処理方法によっては脆弱になる可能性があります。
Learn how to exploit Broadcast Receivers with Drozer.
Exploiting Schemes / Deep links
deep links を手動で探すには、MobSF のようなツールや this one のようなスクリプトを使用できます。
宣言された scheme は adb や browser を使って open できます:
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "scheme://hostname/path?param=value" [your.package.name]
パッケージ名を省略できますと、モバイル端末はそのリンクを開くべきアプリを自動的に起動します.
<!-- Browser regular link -->
<a href="scheme://hostname/path?param=value">Click me</a>
<!-- fallback in your url you could try the intent url -->
<a href="intent://hostname#Intent;scheme=scheme;package=your.package.name;S.browser_fallback_url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com;end">with alternative</a>
実行されるコード
アプリで実行されるコードを見つけるには、deeplink によって呼び出される activity に移動し、関数 onNewIntent を検索してください。
機密情報
deep link を見つけるたびに、URL パラメータ経由で機密データ(パスワードなど)を受け取っていないかを確認してください。なぜなら、他のアプリケーションがdeep link をなりすましてそのデータを盗む可能性があるからです!
Parameters in path
URL のパス内でパラメータを使用している deep link がないか、必ず確認してください。例えば: https://api.example.com/v1/users/{username} のような場合、example://app/users?username=../../unwanted-endpoint%3fparam=value のようにアクセスすることで path traversal を強制できることがあります。
Note that if you find the correct endpoints inside the application you may be able to cause a Open Redirect (if part of the path is used as domain name), account takeover (if you can modify users details without CSRF token and the vuln endpoint used the correct method) and any other vuln. More info about this here.
More examples
interesting bug bounty report はリンク(/.well-known/assetlinks.json)に関する報告です。
Transport Layer Inspection and Verification Failures
- Certificates are not always inspected properly by Android applications. It's common for these applications to overlook warnings and accept self-signed certificates or, in some instances, revert to using HTTP connections.
- Negotiations during the SSL/TLS handshake are sometimes weak, employing insecure cipher suites. This vulnerability makes the connection susceptible to man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, allowing attackers to decrypt the data.
- Leakage of private information is a risk when applications authenticate using secure channels but then communicate over non-secure channels for other transactions. This approach fails to protect sensitive data, such as session cookies or user details, from interception by malicious entities.
Certificate Verification
ここでは certificate verification に焦点を当てます。サーバーの証明書の整合性を検証することはセキュリティ強化のために重要です。不適切な TLS 設定や暗号化されていないチャネルでの機密データ送信は重大なリスクをもたらす可能性があります。サーバー証明書の検証方法や脆弱性への対処手順の詳細については、this resource を参照してください。
SSL Pinning
SSL Pinning は、アプリケーションがサーバーの証明書をアプリ内に保存された既知のコピーと照合して検証するセキュリティ対策です。この手法は MITM 攻撃を防ぐために不可欠です。機密情報を扱うアプリケーションでは SSL Pinning の実装を強く推奨します。
Traffic Inspection
HTTP トラフィックを検査するには、プロキシツールの証明書(例: Burp)をインストールする必要があります。この証明書をインストールしていないと、暗号化されたトラフィックはプロキシで見えない場合があります。カスタム CA 証明書のインストール手順については、click here を参照してください。
API Level 24 and above をターゲットにしたアプリケーションは、プロキシの CA 証明書を受け入れるように Network Security Config を修正する必要があります。この手順は暗号化トラフィックを検査する上で重要です。Network Security Config の変更方法については、refer to this tutorial を参照してください。
If Flutter is being used you need to to follow the instructions in this page. This is becasue, just adding the certificate into the store won't work as Flutter has its own list of valid CAs.
Static detection of SSL/TLS pinning
ランタイムでのバイパスを試みる前に、APK 内で pinning が適用されている箇所を素早くマップしてください。静的検出はフックやパッチの計画を助け、適切なコードパスに集中するのに役立ちます。
Tool: SSLPinDetect
- Open-source static-analysis utility that decompiles the APK to Smali (via apktool) and scans for curated regex patterns of SSL/TLS pinning implementations.
- Reports exact file path, line number, and a code snippet for each match.
- Covers common frameworks and custom code paths: OkHttp CertificatePinner, custom javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager.checkServerTrusted, SSLContext.init with custom TrustManagers/KeyManagers, and Network Security Config XML pins.
Install
- Prereqs: Python >= 3.8, Java on PATH, apktool
git clone https://github.com/aancw/SSLPinDetect
cd SSLPinDetect
pip install -r requirements.txt
使い方
# Basic
python sslpindetect.py -f app.apk -a apktool.jar
# Verbose (timings + per-match path:line + snippet)
python sslpindetect.py -a apktool_2.11.0.jar -f sample/app-release.apk -v
パターンルールの例 (JSON) プロプライエタリ/カスタムの pinning スタイルを検出するために、signatures を使用または拡張します。独自の JSON を読み込んで大規模にスキャンできます。
{
"OkHttp Certificate Pinning": [
"Lcom/squareup/okhttp/CertificatePinner;",
"Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner;",
"setCertificatePinner"
],
"TrustManager Override": [
"Ljavax/net/ssl/X509TrustManager;",
"checkServerTrusted"
]
}
Notes and tips
- 大規模なアプリを高速にスキャンするには、マルチスレッディングとメモリマップドI/Oを利用する。プリコンパイルされたregexはオーバーヘッドや偽陽性を減らす。
- Pattern collection: https://github.com/aancw/smali-sslpin-patterns
- 次にトリアージすべき典型的な検出対象:
- OkHttp: CertificatePinner の使用、setCertificatePinner、okhttp3/okhttp パッケージ参照
- Custom TrustManagers: javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager、checkServerTrusted のオーバーライド
- Custom SSL contexts: SSLContext.getInstance + SSLContext.init とカスタムマネージャー
- Declarative pins は res/xml の network security config や manifest の参照にある
- 一致した箇所を活用して、動的テスト前に Frida hooks、static patches、または設定レビューを計画する。
Bypassing SSL Pinning
SSL Pinning が実装されている場合、HTTPS トラフィックを解析するためにそれをバイパスする必要がある。これを行うための様々な手法が存在する:
- 自動で apk-mitm を使って apk を変更し、SSLPinning をバイパスする。 この方法の最大の利点は、SSL Pinning をバイパスするために root が不要なことだが、アプリを削除して新しいものを再インストールする必要があり、常に動作するとは限らない。
- この保護を回避するために Frida(下記参照)を使うこともできる。Burp+Frida+Genymotion の使用ガイド: https://spenkk.github.io/bugbounty/Configuring-Frida-with-Burp-and-GenyMotion-to-bypass-SSL-Pinning/
- objection を使って 自動的に SSL Pinning をバイパスすることも試せる::
objection --gadget com.package.app explore --startup-command "android sslpinning disable" - MobSF dynamic analysis を使って 自動的に SSL Pinning をバイパスすることも試せる(下記参照)
- それでもキャプチャできていないトラフィックがあると思われる場合、iptables を使ってトラフィックを burp に転送してみることができる。この記事を読む: https://infosecwriteups.com/bypass-ssl-pinning-with-ip-forwarding-iptables-568171b52b62
Looking for Common Web Vulnerabilities
アプリ内で一般的な Web 脆弱性を検索することも重要である。これらの脆弱性の特定や緩和に関する詳細はこの要約の範囲を超えるが、他所で広く扱われている。
Frida
Frida は、開発者、リバースエンジニア、セキュリティ研究者のための動的インストルメンテーションツールキットである。
実行中のアプリにアクセスしてランタイムでメソッドをフックし、挙動を変更したり、値を変更・抽出したり、別のコードを実行したりできる。
Android アプリを pentest するなら Frida の使い方を知っておく必要がある。
- Learn how to use Frida: Frida tutorial
- Frida を使った操作のための「GUI」的なもの: https://github.com/m0bilesecurity/RMS-Runtime-Mobile-Security
- Frida の利用を自動化するには Ojection が便利: https://github.com/sensepost/objection , https://github.com/dpnishant/appmon
- いくつかの Awesome Frida スクリプトはこちらで見つかる: https://codeshare.frida.re/
- Frida をロードして anti-debugging / anti-frida 機構を回避することを試みる: https://erfur.github.io/blog/dev/code-injection-without-ptrace(ツール: linjector)
Anti-instrumentation & SSL pinning bypass workflow
{{#ref}} android-anti-instrumentation-and-ssl-pinning-bypass.md {{#endref}}
Dump Memory - Fridump
アプリがパスワードやニーモニックなど、本来メモリに保持すべきでない機密情報をメモリ内に保持していないかを確認する。
Fridump3 を使うと、次のようにしてアプリのメモリをダンプできる:
# With PID
python3 fridump3.py -u <PID>
# With name
frida-ps -Uai
python3 fridump3.py -u "<Name>"
これによりメモリが ./dump フォルダにダンプされ、そこで次のようなコマンドで grep できます:
strings * | grep -E "^[a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+ [a-z]+$"
Keystore内の機密データ
AndroidではKeystoreが機密データを保存する最良の場所ですが、十分な権限があればそれでもアクセス可能です。アプリはここに平文の機密データを保存する傾向があるため、pentestsはroot userとして確認する必要があります。また、デバイスに物理的にアクセスできる人物がこれらのデータを盗む可能性があります。
たとえアプリがKeystoreにデータを保存していても、そのデータは暗号化されているべきです。
To access the data inside the Keystore you could use this Frida script: https://github.com/WithSecureLabs/android-keystore-audit/blob/master/frida-scripts/tracer-cipher.js
frida -U -f com.example.app -l frida-scripts/tracer-cipher.js
Fingerprint/Biometrics Bypass
以下のFridaスクリプトを使用すると、Androidアプリが特定の機密領域を保護するために実行している bypass fingerprint authentication を回避できる可能性があります:
frida --codeshare krapgras/android-biometric-bypass-update-android-11 -U -f <app.package>
バックグラウンド画像
アプリをバックグラウンドに入れると、Android は アプリケーションのスナップショット を保存します。これによりフォアグラウンドに戻したときにアプリより先にその画像を読み込んで、アプリの起動が速く見えるようになります。
しかし、このスナップショットに 機密情報 が含まれている場合、スナップショットにアクセスできる者が その情報を盗む 可能性があります(アクセスするには root が必要な点に注意してください)。
スナップショットは通常次の場所に保存されます: /data/system_ce/0/snapshots
Android は FLAG_SECURE を設定してスクリーンショットの取得を防ぐ方法 を提供しています。このフラグを使用するとウィンドウの内容がセキュアとして扱われ、スクリーンショットに表示されたり安全でないディスプレイで表示されるのを防ぎます。
getWindow().setFlags(LayoutParams.FLAG_SECURE, LayoutParams.FLAG_SECURE);
Android アプリケーション解析ツール
このツールは、動的解析中に複数のツールを管理するのに役立ちます: https://github.com/NotSoSecure/android_application_analyzer
Intent Injection
開発者はしばしば activity、service、broadcast receiver のようなプロキシコンポーネントを作成し、これらの Intent を処理して startActivity(...) や sendBroadcast(...) のようなメソッドに渡しますが、これは危険を伴うことがあります。
危険は、攻撃者がこれらの Intent を誤誘導して non-exported なアプリコンポーネントをトリガーしたり、センシティブな content providers にアクセスさせたりできる点にあります。顕著な例としては、WebView コンポーネントが URL を Intent.parseUri(...) を通じて Intent オブジェクトに変換し、それを実行して結果的に悪意ある Intent 注入を許してしまうケースがあります。
Essential Takeaways
- Intent Injection は web の Open Redirect 脆弱性に似ています。
- エクスプロイトは Intent オブジェクトを extras として渡し、それがリダイレクトされて安全でない操作を実行させることを含みます。
- 非エクスポートのコンポーネントや content providers が攻撃者にさらされる可能性があります。
WebViewの URL→Intent変換により、意図しない動作が誘発されることがあります。
Android Client Side Injections and others
おそらくこの種の脆弱性は Web で既に聞いたことがあるでしょう。Android アプリケーションでは次の脆弱性に特に注意する必要があります:
- SQL Injection: 動的なクエリや Content-Providers を扱う場合は、パラメータ化されたクエリを使用していることを確認してください。
- JavaScript Injection (XSS): 任意の WebViews で JavaScript と Plugin のサポートが無効になっていることを確認してください(デフォルトで無効)。 More info here.
- Local File Inclusion: WebViews のファイルシステムへのアクセスは無効にするべきです(デフォルトで有効) -
(webview.getSettings().setAllowFileAccess(false);). More info here. - Eternal cookies: 多くの場合、Android アプリがセッションを終了しても cookie が取り消されなかったり、ディスクに保存されてしまったりします。
- Secure Flag in cookies
自動解析
MobSF
静的解析
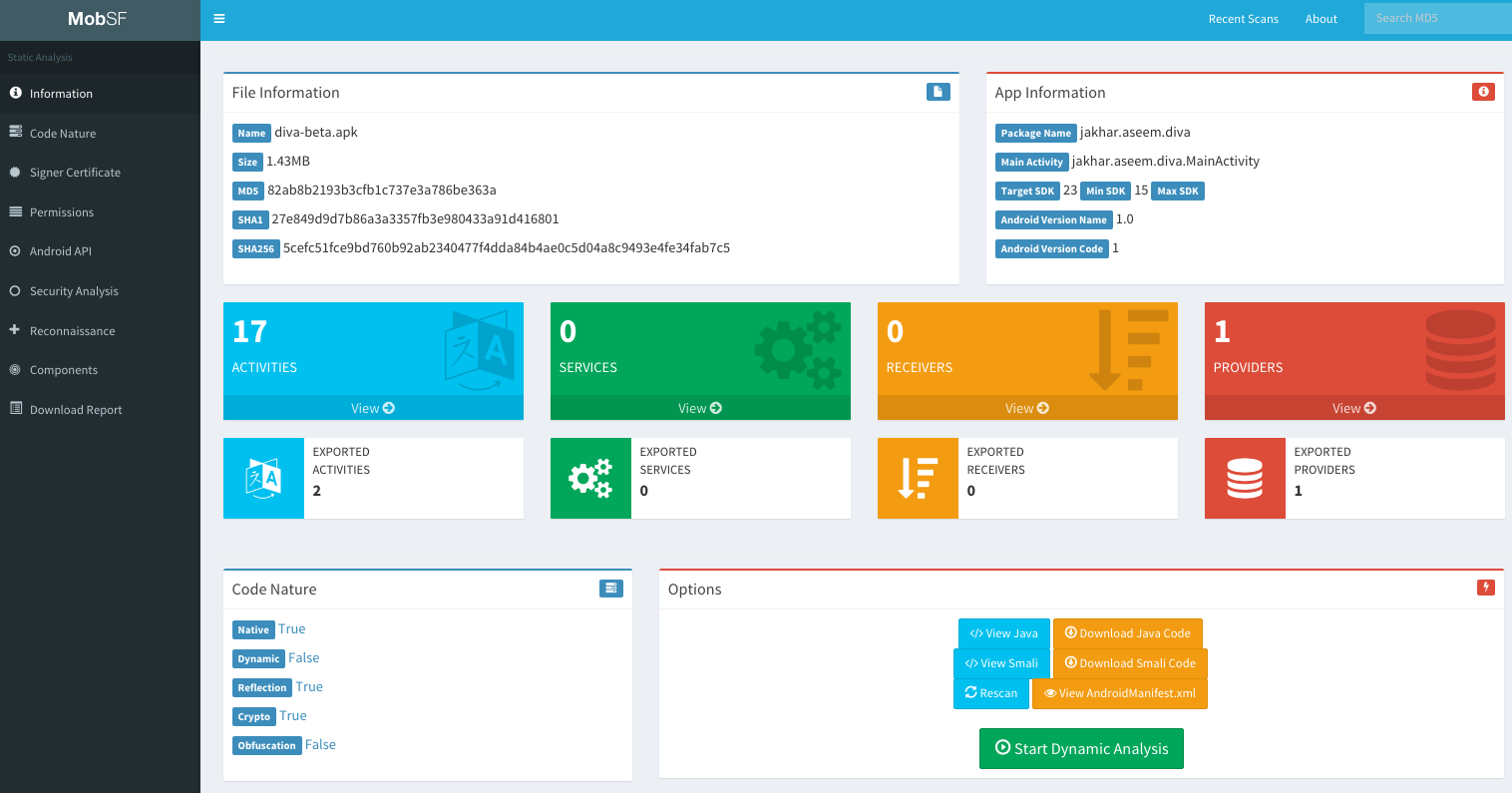
アプリケーションの脆弱性評価 を、使いやすいウェブベースのフロントエンドで行えます。動的解析も実行できます(ただし環境の準備が必要です)。
docker pull opensecurity/mobile-security-framework-mobsf
docker run -it -p 8000:8000 opensecurity/mobile-security-framework-mobsf:latest
Notice that MobSF can analyse Android(apk), IOS(ipa) and Windows(apx) applications (Windows applications must be analyzed from a MobSF installed in a Windows host).
Also, if you create a ZIP file with the source code if an Android or an IOS app (go to the root folder of the application, select everything and create a ZIPfile), it will be able to analyse it also.
MobSF also allows you to diff/Compare analysis and to integrate VirusTotal (you will need to set your API key in MobSF/settings.py and enable it: VT_ENABLED = TRUE VT_API_KEY = <Your API key> VT_UPLOAD = TRUE). You can also set VT_UPLOAD to False, then the hash will be upload instead of the file.
Assisted Dynamic analysis with MobSF
MobSF can also be very helpful for dynamic analysis in Android, but in that case you will need to install MobSF and genymotion in your host (a VM or Docker won't work). Note: You need to start first a VM in genymotion and then MobSF.
The MobSF dynamic analyser can:
- Dump application data (URLs, logs, clipboard, screenshots made by you, screenshots made by "Exported Activity Tester", emails, SQLite databases, XML files, and other created files). All of this is done automatically except for the screenshots, you need to press when you want a screenshot or you need to press "Exported Activity Tester" to obtain screenshots of all the exported activities.
- Capture HTTPS traffic
- Use Frida to obtain runtime information
From android versions > 5, it will automatically start Frida and will set global proxy settings to capture traffic. It will only capture traffic from the tested application.
Frida
By default, it will also use some Frida Scripts to bypass SSL pinning, root detection and debugger detection and to monitor interesting APIs.
MobSF can also invoke exported activities, grab screenshots of them and save them for the report.
To start the dynamic testing press the green bottom: "Start Instrumentation". Press the "Frida Live Logs" to see the logs generated by the Frida scripts and "Live API Monitor" to see all the invocation to hooked methods, arguments passed and returned values (this will appear after pressing "Start Instrumentation").
MobSF also allows you to load your own Frida scripts (to send the results of your Friday scripts to MobSF use the function send()). It also has several pre-written scripts you can load (you can add more in MobSF/DynamicAnalyzer/tools/frida_scripts/others/), just select them, press "Load" and press "Start Instrumentation" (you will be able to see the logs of that scripts inside "Frida Live Logs").
Moreover, you have some Auxiliary Frida functionalities:
- Enumerate Loaded Classes: It will print all the loaded classes
- Capture Strings: It will print all the capture strings while using the application (super noisy)
- Capture String Comparisons: Could be very useful. It will show the 2 strings being compared and if the result was True or False.
- Enumerate Class Methods: Put the class name (like "java.io.File") and it will print all the methods of the class.
- Search Class Pattern: Search classes by pattern
- Trace Class Methods: Trace a whole class (see inputs and outputs of all methods of th class). Remember that by default MobSF traces several interesting Android Api methods.
Once you have selected the auxiliary module you want to use you need to press "Start Intrumentation" and you will see all the outputs in "Frida Live Logs".
Shell
Mobsf also brings you a shell with some adb commands, MobSF commands, and common shell commands at the bottom of the dynamic analysis page. Some interesting commands:
help
shell ls
activities
exported_activities
services
receivers
HTTP ツール
http トラフィックがキャプチャされると、キャプチャしたトラフィックの見づらい表示を「HTTP(S) Traffic」ボトムで、より見やすい表示を「Start HTTPTools」緑色のボタンで確認できます。後者から、キャプチャされたリクエストを プロキシ(Burp や Owasp ZAP など)に 送信することができます。
手順: Burp を起動 --> Intercept をオフ --> MobSB HTTPTools でリクエストを選択 --> 「Send to Fuzzer」を押す --> プロキシアドレスを選択 (http://127.0.0.1:8080\)。
MobSF で dynamic analysis を終えたら、「Start Web API Fuzzer」を押して fuzz http requests を実行し、脆弱性を探すことができます。
Tip
MobSF で dynamic analysis を行った後、プロキシ設定が誤って構成され、GUI から修正できない場合があります。プロキシ設定は以下で修正できます:
adb shell settings put global http_proxy :0
Inspeckage を使った支援付き動的解析
ツールは Inspeckage から入手できます。
このツールは一部の Hooks を利用して、dynamic analysis 実行中にアプリケーション内で what is happening in the application を把握させてくれます。
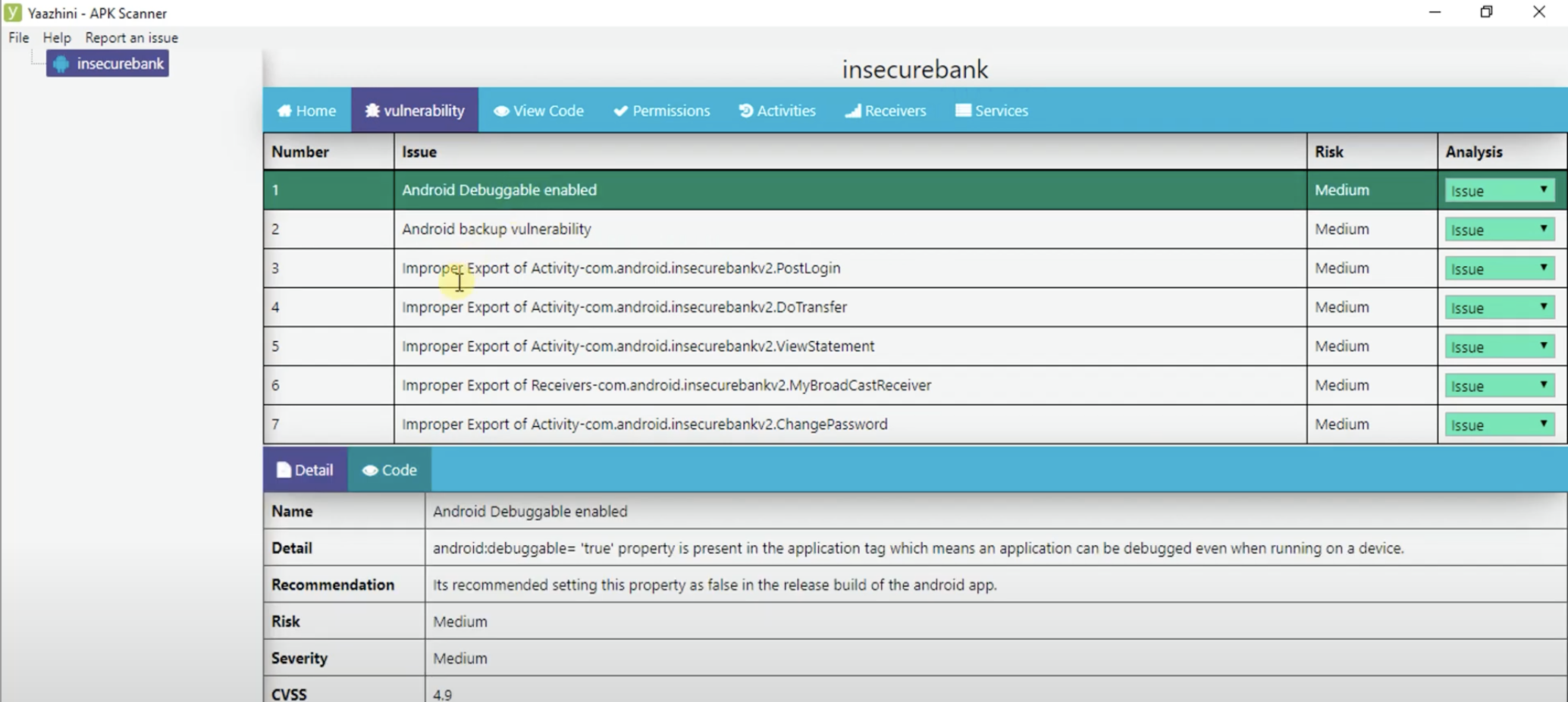
Yaazhini
GUI を使った静的解析を行うための優れたツールです
Qark
このツールは、security related Android application vulnerabilities を、source code または packaged APKs のいずれでも検出するよう設計されています。さらに、発見された一部の脆弱性(Exposed activities、intents、tapjacking など)を悪用するための、"Proof-of-Concept" としてデプロイ可能な APK や ADB commands を作成することもできます。Drozer と同様に、テストデバイスを root する必要はありません。
pip3 install --user qark # --user is only needed if not using a virtualenv
qark --apk path/to/my.apk
qark --java path/to/parent/java/folder
qark --java path/to/specific/java/file.java
ReverseAPK
- 抽出したすべてのファイルを表示し、参照を容易にする
- APKファイルを自動的にJavaおよびSmali形式にデコンパイルする
- AndroidManifest.xmlを解析して一般的な脆弱性や挙動を検出する
- 一般的な脆弱性や挙動に対する静的ソースコード解析
- デバイス情報
- など
reverse-apk relative/path/to/APP.apk
SUPER Android Analyzer
SUPER は Windows、MacOS X、Linux で使用できるコマンドラインアプリケーションで、.apk ファイルを解析して脆弱性を探します。これは APK を展開し、一連のルールを適用して脆弱性を検出することで行われます。
すべてのルールは rules.json ファイルに集約されており、各企業やテスターは独自のルールを作成して必要な解析を行えます。
最新のバイナリは download page からダウンロードしてください。
super-analyzer {apk_file}
StaCoAn
StaCoAnはモバイルアプリケーションに対する static code analysis を行う開発者、bugbounty hunters、ethical hackers を支援する crossplatform ツールです。
コンセプトは、モバイルアプリのファイル(.apk または .ipa ファイル)を StaCoAn アプリにドラッグ&ドロップすると、視覚的で持ち運び可能なレポートを生成してくれる、というものです。設定や wordlists を調整してカスタマイズされた体験を得られます。
ダウンロード latest release:
./stacoan
AndroBugs
AndroBugs Frameworkは、Androidアプリケーションの潜在的なセキュリティ脆弱性を開発者やハッカーが発見するのを支援する脆弱性解析システムです。
Windows releases
python androbugs.py -f [APK file]
androbugs.exe -f [APK file]
Androwarn
Androwarn は、Android アプリケーションによって発生する潜在的な悪意ある振る舞いを検出し、ユーザーに警告することを主な目的としたツールです。
検出は、アプリケーションの Dalvik バイトコードを Smali として表現したものに対する static analysis を、androguard ライブラリで行います。
このツールは、「悪質な」アプリケーションの一般的な挙動 を検出します。例: Telephony identifiers exfiltration, Audio/video flow interception, PIM data modification, Arbitrary code execution...
python androwarn.py -i my_application_to_be_analyzed.apk -r html -v 3
MARA Framework
MARA はモバイルアプリの逆解析および解析のフレームワークです。一般的に使用されるモバイルアプリの逆解析・解析ツールをまとめ、OWASP のモバイルセキュリティ脅威に対するテストを支援します。目的は、この作業をモバイルアプリ開発者やセキュリティ専門家にとってより簡単で扱いやすくすることです。
It is able to:
- さまざまなツールを使用して Java および Smali コードを抽出する
- 以下のツールを使って APK を解析する: smalisca, ClassyShark, androbugs, androwarn, APKiD
- regexps を使って APK からプライベート情報を抽出する
- Manifest を解析する
- 発見したドメインを以下で解析する: pyssltest, testssl and whatweb
- [apk-deguard.com] を使って APK の deobfuscate を行う
Koodous
マルウェア検出に有用: https://koodous.com/
Obfuscating/Deobfuscating code
使用するサービスや設定によって、コードの難読化によってシークレット(秘密情報)が難読化される場合とされない場合があることに注意してください。
ProGuard
From Wikipedia: ProGuard は Java コードを縮小、最適化、難読化するオープンソースのコマンドラインツールです。バイトコードを最適化し、未使用の命令を検出して削除することができます。ProGuard はフリーソフトウェアで、GNU General Public License, version 2 の下で配布されています。
ProGuard は Android SDK の一部として配布され、アプリを release モードでビルドする際に動作します。
DexGuard
APK を deobfuscate するためのステップバイステップガイドは https://blog.lexfo.fr/dexguard.html を参照してください。
(そのガイドによると) 最後に確認したときの Dexguard の動作モードは次の通りでした:
- リソースを InputStream として読み込む;
- 結果を FilterInputStream を継承したクラスに渡して復号する;
- リバースエンジニアの数分の時間を浪費させるための無意味な難読化を行う;
- 復号された結果を ZipInputStream に渡して DEX ファイルを取得する;
- 最後に生成された DEX を
loadDexメソッドを使って Resource として読み込む。
DeGuard
DeGuard は Android の難読化ツールによって行われた難読化プロセスを逆にします。これにより、コードの検査やライブラリの推定など、さまざまなセキュリティ解析が可能になります。
難読化された APK を彼らのプラットフォームにアップロードすることができます。
[Deobfuscate android App]https://github.com/In3tinct/deobfuscate-android-app
This is a LLM tool to find any potential security vulnerabilities in android apps and deobfuscate android app code. Uses Google's Gemini public API.
Simplify
It is a generic android deobfuscator. Simplify virtually executes an app to understand its behavior and then tries to optimize the code so it behaves identically but is easier for a human to understand. Each optimization type is simple and generic, so it doesn't matter what the specific type of obfuscation is used.
APKiD
APKiD は how an APK was made に関する情報を提供します。多くの compilers, packers, obfuscators やその他の変わったものを識別します。Android 向けの [PEiD] と言えます。
Manual
Read this tutorial to learn some tricks on how to reverse custom obfuscation
Labs
Androl4b
AndroL4b は ubuntu-mate ベースの Android セキュリティ仮想マシンで、reverse engineering や malware analysis のための最新フレームワーク、チュートリアル、ラボをさまざまなセキュリティ研究者やエンジニアから収集して含んでいます。
References
- https://owasp.org/www-project-mobile-app-security/
- https://appsecwiki.com/#/ 素晴らしいリソース一覧です
- https://maddiestone.github.io/AndroidAppRE/ Android クイックコース
- https://manifestsecurity.com/android-application-security/
- https://github.com/Ralireza/Android-Security-Teryaagh
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PMKnPaGWxtg&feature=youtu.be&ab_channel=B3nacSec
- SSLPinDetect: Advanced SSL Pinning Detection for Android Security Analysis
- SSLPinDetect GitHub
- smali-sslpin-patterns
- Build a Repeatable Android Bug Bounty Lab: Emulator vs Magisk, Burp, Frida, and Medusa
Yet to try
{{#include ../../banners/hacktricks-training.md}}